Unveiling the Future: Transforming Real-World Assets Through Blockchain Tokenization

Executive Summary
About RWA Tokenization
Tokenization of real-world assets refers to the process of converting rights to an asset or income generated by the asset into a digital token on a blockchain. Types of real-world assets that can be tokenized include private equity, contracts, real estate, capital assets, art and collectibles, commodities, financial instruments, intellectual property and others.
Tokenization Value Proposition
Liquidity: One of the primary benefits of tokenizing assets is increased liquidity. Many real-world assets like real estate, art, or private equity can be illiquid, meaning they can’t be easily sold or traded. By dividing the asset into tokens, owners can sell portions of their assets, making these assets more liquid.
Fractional Ownership: Tokenization allows assets to be divided into smaller fractions. For example, a piece of real estate could be divided into thousands of tokens, allowing investors to buy a “fraction” of the property rather than the entire building.
Access to Capital: Tokenizing assets can open up investment opportunities to a broader group of people and provide access to a global pool of investors, transcending geographic boundaries.
Token Based Incentives: By offering tokens as rewards, businesses can motivate and drive contributions, ensuring active participation and fostering a sense of ownership among contributors or stakeholders. Distributing tokens to consumers in exchange for their engagement, usage, or consumption fosters loyalty.
Types of Assets
Here are some examples of assets which can be tokenized and their potential use-cases:
Businesses and Companies: Tokenizing a business or company can allow for a new avenue of raising capital through security token offerings (STOS). It can also provide increased transparency to shareholders, simplify shareholder voting, and offer quicker and more cost-effective trading and settlement of shares.
Real Estate: By converting real estate into digital tokens, you can enable fractional ownership. This can make traditionally expensive real estate investments more accessible to a broader audience, improve liquidity in the real estate market, and simplify processes such as property transactions, leasing, and management.
Intellectual Property: Intellectual property rights (like patents or copyrights) can be tokenized to enable micro-licensing or fractional ownership.
Physical Assets: Tokenizing physical assets can enable their fractional ownership or lease. It can also simplify the process of transferring ownership, tracking the asset’s provenance, and automating processes through smart contracts.
Financial Instruments: Financial instruments, such as bonds or derivatives, can benefit from increased liquidity when tokenized. Additionally, tokenization can simplify issuance, reduce intermediaries, and offer programmable functionalities (e.g., automated interest payments through smart contracts).
Art and Collectibles: Tokenizing art or collectibles allows for fractional ownership of valuable items. This means that more people can invest in or own a part of a rare artwork or collectible.
Contracts: By tokenizing a contract’s income stream, investors can obtain fractional ownership of the revenue or profits generated by that contract.
Commodities: Tokenizing commodities (like gold or oil) allows for easier trading and ownership. Investors can own fractions of commodities, improving accessibility.
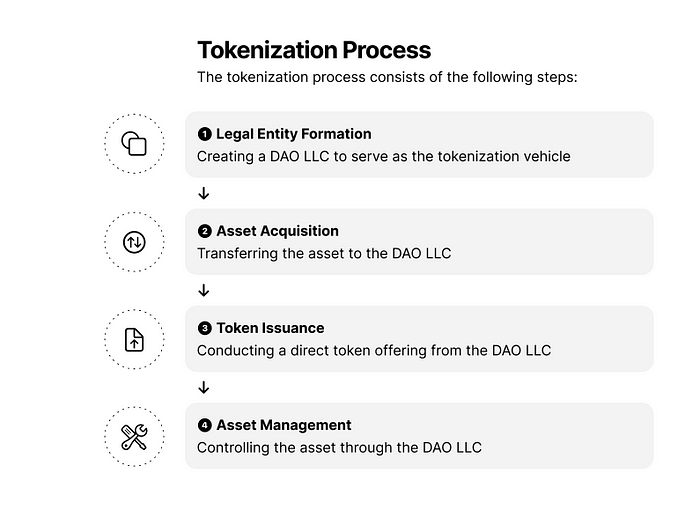
Legal Entity Formation
DAO LLC Overview
A Wyoming DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) LLC is a specific type of Limited Liability Company recognized in the state of Wyoming that is structured to operate on blockchain technology. House Bill 0071 (HB0071) titled “Wyoming Decentralized Autonomous Organizations,” which was introduced in the Wyoming Legislature in 2021, amends Wyoming’s Limited Liability Company Act to provide for the establishment of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) as limited liability companies. DAO LLC governance is based on pre- defined rules, consensus mechanisms, or codes inherent in their underlying smart contracts.
Members of a DAO LLC enjoy limited liability protection, similar to members of traditional LLCs.This means that members are generally not personally liable for the debts or actions of the DAO LLC. A DAO LLC can enter into contracts, hold assets, and sue or be sued, just like traditional LLCs.
Tax Reporting
At the federal level, a Wyoming DAO LLC would typically be treated as a pass-through entity (like other LLCs) unless it elects to be taxed as a corporation. This means the LLC itself is not subject to federal income tax. Instead, the income, deductions, and credits of the LLC “pass through” to its members, who report this information on their personal tax returns.
One of the advantages of forming an LLC in Wyoming is the favourable state tax environment. Wyoming does not have a state income tax, so the state does not tax the income of LLCs or their members. However, if the members of the LLC reside in or derive income from other states, they may still be subject to taxation in those states.
Navigating DAO LLC Taxation: A Guide to Entity Types and Reporting
In the intricate realm of DAO LLCs, understanding the tax implications of different entity types is crucial. Whether you’re operating as a Single Member DAO LLC, a Multi Member DAO LLC, a DAO LLC with C-corp Election, or a Foreign-Owned DAO LLC, each entity type comes with its own set of rules and reporting obligations.
Single Member DAO LLC: The Disregarded Entity
Entity Type: Single Member DAO LLC
Rules:
A Single Member DAO LLC is akin to a “disregarded entity” for federal tax purposes. In simpler terms, it means the entity itself doesn’t bear the brunt of taxes at the company level. Instead, all financial aspects flow through to the single member (owner) and find a place on the individual’s personal tax return.
Reporting:
The income or loss of the Single Member DAO LLC is seamlessly reported on the member’s personal tax return. Schedule C captures the intricacies if the DAO LLC’s activities are trade or business-related.
Multi Member DAO LLC: Collaborative Tax Landscape
Entity Type: Multi Member DAO LLC
Rules:
Contrary to its single-member counterpart, a Multi Member DAO LLC doesn’t pay federal income taxes at the company level. Instead, it’s mandated to file an annual informational return, Form 1065 (U.S. Return of Partnership Income), outlining comprehensive financial details.
Reporting:
After filing Form 1065, each member receives a Schedule K-1, summarizing their distributive share of the DAO LLC’s income or loss. This information is then integrated into individual tax returns.
DAO LLC with C-corp Election: Opting for Corporate Taxation
Entity Type: DAO LLC with C-corp Election
Rules:
Opting for corporate taxation is a choice for a Single Member DAO LLC. This election involves filing IRS Form 8832. Under this scenario, the DAO LLC faces taxation at the corporate level, and any dividends distributed to the member undergo taxation on the individual’s personal tax return.
Reporting:
Annual filing obligation with Form 1120 (U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return) becomes imperative, detailing income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits.
Foreign-Owned DAO LLC: Navigating Global Tax Considerations
Entity Type: Foreign-Owned DAO LLC
Rules:
For a foreign-owned DAO LLC engaged in a U.S. trade or business, income effectively connected with that trade or business (ECI) is subject to U.S. federal income tax. Reporting obligations differ, with individual owners using Form 1040-NR and foreign corporations resorting to Form 1120-F.
Reporting:
Form 5472, an Information Return, becomes a mandatory filing for foreign-owned DAO LLCs. It reports specific transactions between the LLC and its foreign owner or other foreign-related parties.
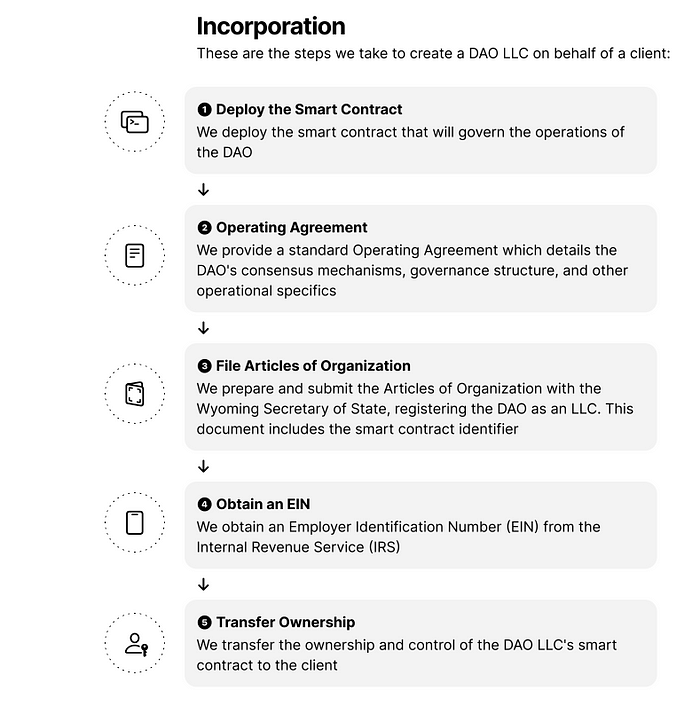
Asset Acquisition
Acquisition Methods
A DAO LLC can acquire assets in a manner similar to traditional LLCs. Depending on the type of instrument being offered, the acquisition can take place prior to or after the fundraising event. Here’s a summary of how a DAO LLC might acquire various types of assets:
Real Estate: DAO LLCs have the power to directly purchase real estate by allocating funds from their treasury to the acquisition. The property title is securely held in the name of the DAO LLC
Intellectual Property: The acquisition of patents, trademarks, copyrights, and other intellectual property rights is within the purview of DAO LLCs. These rights are seamlessly transferred to and held by the DAO LLC, fostering an environment conducive to creativity and innovation.
Physical Assets: DAO LLCs can leverage their funds to purchase physical assets, ensuring ownership and utilization for operational objectives. For assets deemed unnecessary to own outright, strategic lease or rental agreements provide flexibility without compromising financial prudence.
Financial Instruments: DAO LLCs possess the capability to diversify into financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, or other securities through traditional financial markets.
Companies: Operating with a business-oriented mindset, DAO LLCs can engage in mergers or acquisitions, utilizing their funds to acquire other businesses or companies.
Art and Collectibles: With the ability to directly acquire art or collectibles, DAO LLCs contribute to cultural investments.
Contracts: DAO LLCs can enter into various agreements, including licensing agreements, service agreements, partnership agreements, as well as leases or rental contracts.
Token Offerings
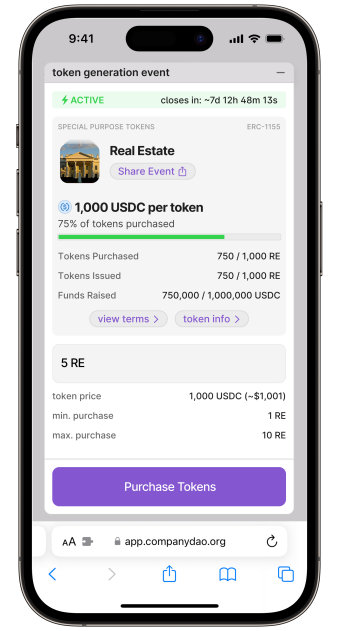
Token Generation Events
DAO LLCS which operate on the Company DAO protocol can conduct Direct Token Offerings from their smart contracts, using the Company DAO protocol to launch a Token Generation Event. The Token Generation Event can be accessed through a token purchasing form with KYC and payment processing integrations in the web app. This type of offering allows the DAO LLC to raise capital, distribute ownership stakes, or represent specific rights or assets through the issuance of tokens directly to investors or participants.
Types of Offerings
Direct Public Offering: In a DPO, tokens are offered directly to the public without intermediaries like underwriters. This model is not limited to the crypto world and has been used traditionally by companies going public.
Initial DEX Offering: IDOS are token offerings that occur on decentralized exchange (DEX) platforms. These offerings leverage the decentralized nature of DEXS to provide immediate liquidity and trading of the tokens.
Initial Exchange Offering: In an IEO, the token offering is conducted on a cryptocurrency exchange platform. Unlike ICOs, where the project team sells tokens directly to investors, in IEOS, the exchange takes on the role of counterparty and facilitates the sale.
Token Standards
Tokens can represent various forms of rights, such as equity, membership, revenue-sharing, or access to specific services or products. The DAO LLC can issue tokens from its smart contracts using different technical standards to meet business requirements:
ERC-20: The ERC-20 standard is one of the earliest and most widely adopted Ethereum token standards for a token with identical and interchangeable units, like currencies or utility tokens
ERC-1155: The ERC-1155 standard, often referred to as a “multi-token” standard, allows for the creation and management of both fungible and non-fungible tokens using a single smart contract
Types of Tokens
Using these token standards, the DAO LLC can create different types of instruments:

Equity Tokens: These tokens represent ownership in an underlying company, much like traditional shares or stocks. By owning an equity token, you might have a stake in the company and may be entitled to dividends, voting rights, or other benefits
Debt Tokens: These are akin to short-term or long-term loans. By purchasing a debt token, you are essentially lending money and in return, you will receive interest payments and eventually the return of the principal
Utility Tokens: Provide a user with access to a product or service
Asset-backed Tokens: These tokens are backed by tangible or intangible assets like gold, art, or collectibles. The value of the token is pegged to the value of the underlying asset.
Fund Tokens: These tokens represent a stake in an investment fund. They can be used to gain exposure to a diversified portfolio without owning the individual assets.
Special Equity: A Wyoming DAO LLC can issue equity tokens (membership interests) that represents a specific asset held by the LLC. This is often referred to as creating a “special class” of membership interests. By doing so, the LLC can allocate the economic benefits, and potentially certain voting rights, derived from that particular asset to the holders of that special class of membership interests.
Promissory Note Token: This is a debt instrument where the DAO LLC promises to pay the holder an amount based on the profits from a specific asset. It can be structured in many ways, including as a “participation loan,” where the payout is tied to the performance of the asset.
Royalty Token: If the asset is something like intellectual property, the DAO LLC could enter into a royalty agreement where the holder receives a portion of revenues or profits from the exploitation of that asset.
Economic Rights Units: Some entities use this kind of structure to grant economic benefits without conferring ownership or voting rights. ERUS would entitle holders to a share of profits or distributions but wouldn’t make them members of the DAO LLC.
Promissory Note Token: This is a debt instrument where the DAO LLC promises to pay the holder an amount based on the profits from a specific asset. It can be structured in many ways, including as a “participation loan,” where the payout is tied to the performance of the asset.
Deal Structuring
The DAO LLC use several instruments to define the terms of its token sale or transfer of tokens:
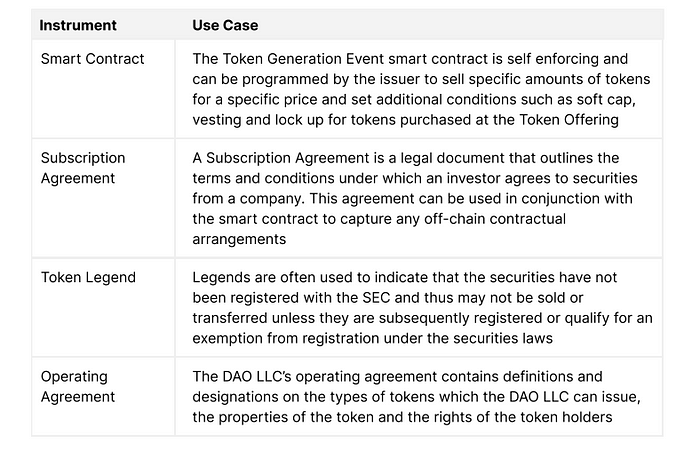
Compliance
Tokens issued by the DAO LLC may be considered securities under federal law. The nature of your tokens, whether they qualify as securities under U.S. law, and the method of their issuance will impact the regulatory requirements. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is responsible for regulating securities offerings, even those made to non-U.S. residents. If your tokens are seen as commodities rather than securities, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) might be the relevant regulatory body.
For tokens which are considered to be securities, there are several exemptions from registration and simplified registration requirements for which the DAO LLC can qualify as an issuer if certain criteria are met:
Reg S : Reg S provides a safe harbor for offerings made outside the U.S. by both U.S. and foreign issuers. It allows them to comply with the registration requirement under the Securities Act of 1933, without having to register with the SEC, provided the offering is conducted outside the U.S. and the securities are sold to non-U.S. persons.
Reg A : Reg A is an exemption from registration requirements for public offerings of securities in the U.S. It is split into two tiers: Tier 1 for offerings up to $20 million and Tier 2 for offerings up to $75 million in a 12-month period. Reg A allows smaller companies to access capital without going through the more rigorous SEC registration process.
Reg D : Allows companies to advertise their securities to the public and raise an unlimited amount of capital in the US, provided they only sell to accredited US investors.
Asset Management
AM Lifecycle
The DAO LLC manages the asset, which might involve overseeing its operations, maintenance, and anything else required to generate income from the asset. Here are some steps in the asset management lifecycle:
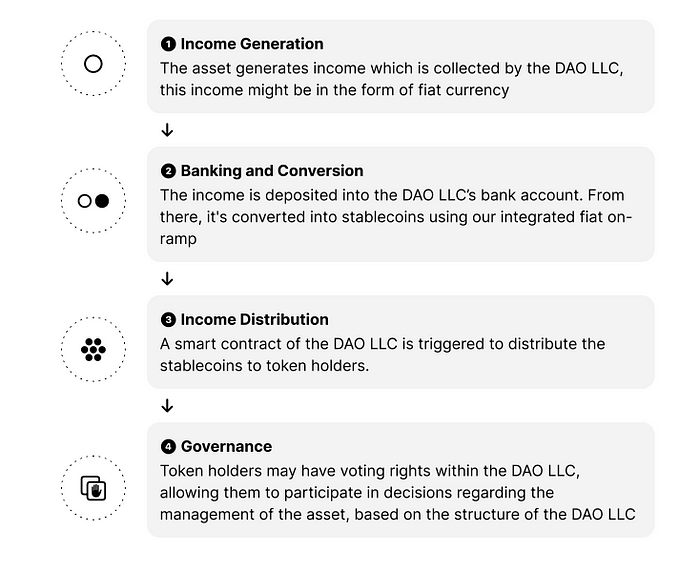
Our Services
▶ DAO LLC Set Up

▶ DAO LLC Management

▶ Tokenization

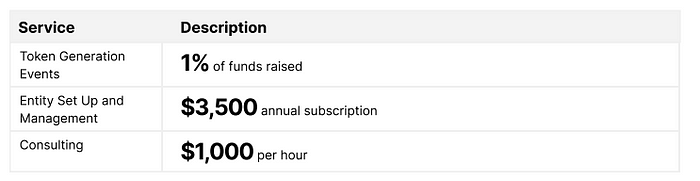
Pricing
Contacts
Email: email@companydao.org
Telegram, WhatsApp: +1 307 217–3127
Website: companydao.org
Community: t.me/cdaogroup

